Fraud Management
For many years, fraud risk examiners have deployed substantial resources to carry on the war against fraud management and yet not much has been achieved.
Accounting fraud and corporate fraud still make headlines almost on a daily basis. Directors of companies go to jail for either committing fraud or for not establishing adequate internal control that will safeguard the assets of a company.
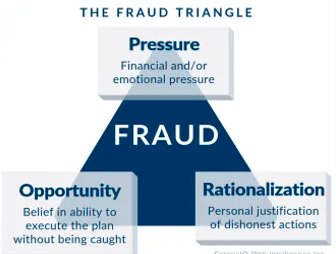
Corporate fraud can be stopped if we spend enough time to find out why fraud takes place in the first place. Then find out the solutions to remove the cause of corporate fraud.
One of the biggest example of frauds in India’s corporate history:- Ramalinga Raju who is the founder and CEO of Satyam Computers, Indias fourth-largest IT services firm, announced on 7th January 2009, that his company had been falsifying its accounts for years, overstating revenues and inflating profits by $1 billion.
What is Corporate Fraud??
Generally, corporate fraud means the activities done by an individual or company in a dishonest or illegal manner. It is an act of deception, an intentional concealment, omission or prevention of truth to gain unlawful advantage or benefits.
The government of India has provided the definition of fraud in Section 447 of the Indian Companies Act 2013 for the first time in Indian corporate history.
Companies are becoming more aware of the need for an internal mechanism to keep a check on the incidents of fraud within the companies (fraud management). Among other measures, policies that support independent and external audits have been ranked as an effective tool to mitigate the risks of fraud. https://clnk.in/komM

Fraud categories :
- Asset misappropriation
- Theft of tangible assets by internal or external parties
- Sales of proprietary information
- Causing improper payments
- Fraudulent accounting and financial reporting
- Manipulation, falsification, alteration of accounting records
- Misrepresentation or intentional omission of amounts
- Misapplication of accounting principles
- Intentionally false, misleading or omitted disclosures
- Corruption
- Making or receiving improper payments
- Offering bribes to public or private officials
- Receiving bribes or other payments
- Aiding and supporting fraud by others
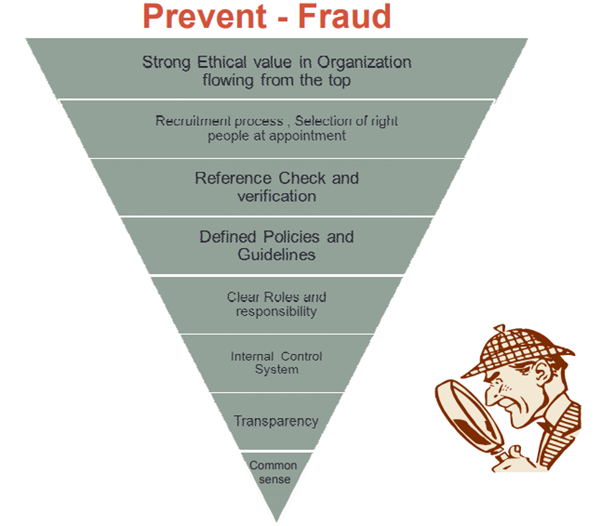
Internal controls prevent and detect fraud
- Active assessment of risk factors by management and follow up on action taken.
- Proper compliance with laws and regulatory guidelines set up by the Indian government.
- Transparency in accounting and financial reporting.
- Company behaviour and ethics code should be developed, documented, and communicated to employees.
- Focus on operational risks. Eg: bribery for supplier selection.
- Identifying key areas of focus particular to ensure efficient use of resources.
- Policy for whistleblowing where management ensures the confidentiality and safety of information providers.
- Monitoring Stock, cash, data theft.